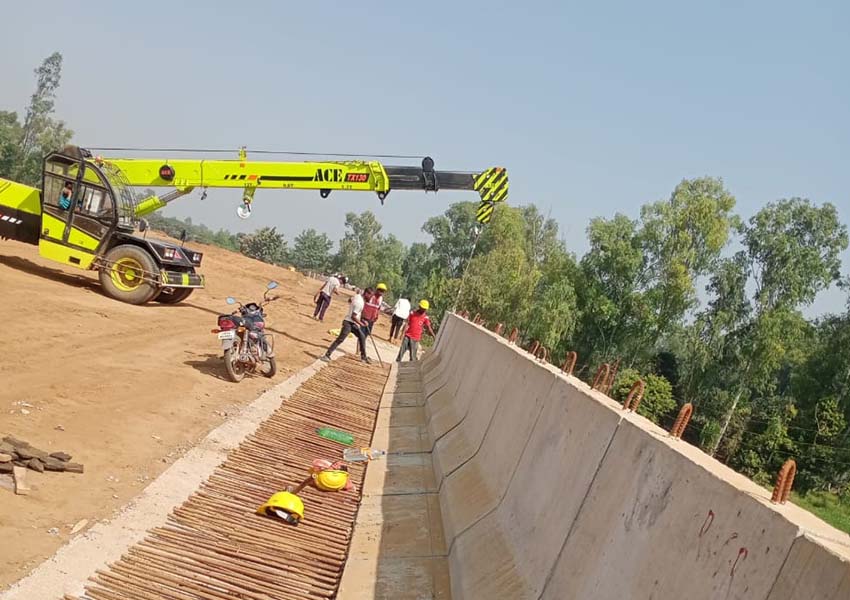
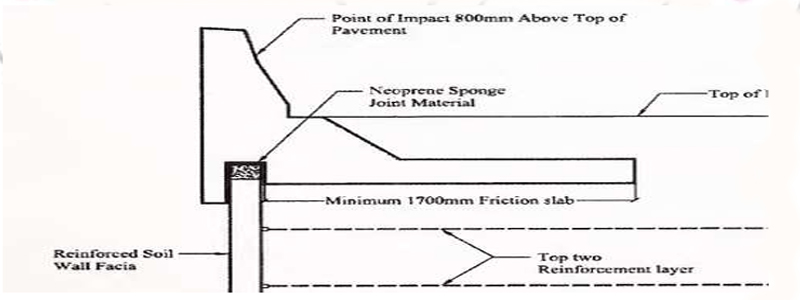
Crash barriers and friction slabs are designed to withstand the impact of vehicles of certain weights at certain angle while traveling at the specified speed. They are expected to guide the vehicle back on the road while keeping the level of damage to vehicle as well as to the barriers within acceptable limits.
Traffic barriers (Crash barriers) are constructed over the front face of the reinforced walls.
Friction Slabs are structural members which extend over a part of the width of the approach embankment of a highway bridge/flyover, to which the crash barriers are anchored (doweled).