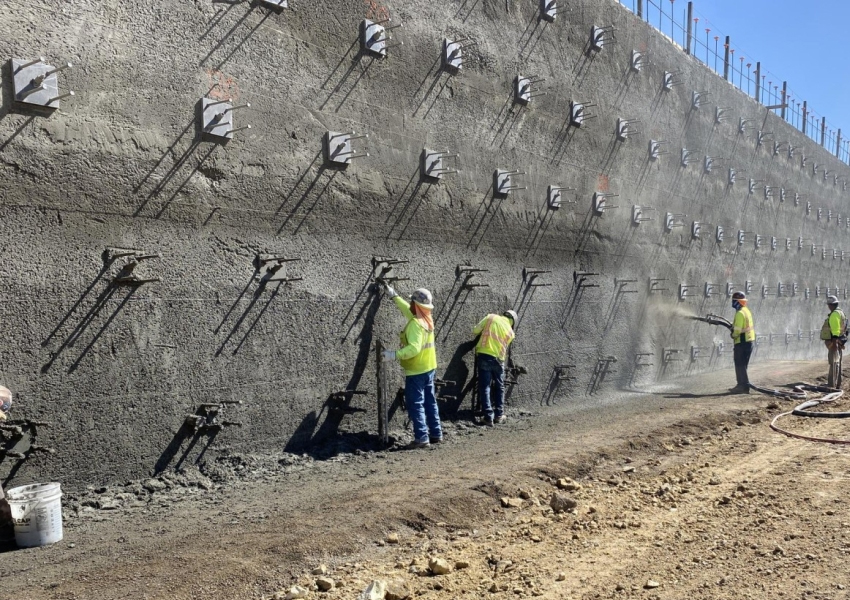
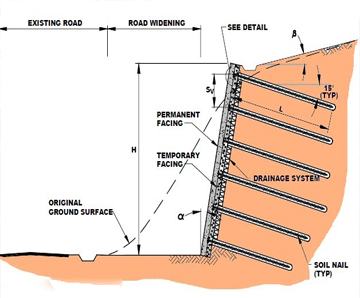
Soil nailing is a ground reinforcement technique used to stabilize slopes, retaining walls, and excavations. It involves inserting slender, high-strength steel bars (nails) into the soil and securing them with grout. This method improves the overall shear strength of the soil and provides immediate stability during construction and long-term support for slopes and structures.
Soil nails are typically installed at regular intervals along the slope or excavation face. After installation, a facing system such as shotcrete, precast panels, or mesh is applied to maintain the surface integrity. This approach allows for cost-effective stabilization without extensive excavation or large retaining structures.
Soil nailing is widely used in civil and geotechnical engineering projects, including highways, bridges, tunnels, and urban excavations. Its main functions include: